
According to RFC, under such a circumstance, the target should respond back with an RST if the port i s closed 2.
In TCP Null Scans, the TCP packets sent don’t have any of the flags set. If the port is closed and it receives an ICMP echo request back which signifies that the port is unreachable.Īpart from these, some less popular scan types which are even “stealthier” than a TCP SYN scan.In such a scenario, the port is marked open It might get a UDP response back which is very rare.If no response is received yet, it sends another UDP packet to double check and if yet again no response is received, it marks the port as open|filtered and moves on Usually there is no response received in which case nmap marks the port as open|filtered.When an UDP packet is sent to a target port, there might be three scenarios : However, the lack of a feedback mechanism makes it difficult to identify open ports. This gives more emphasis on speed than quality. UDP works on the principle “Fire and Forget” which means that it sends packets directed to targets at certain ports and hopes that they would make it. This means that there’s no “feedback mechanism” like TCP. UDP scans are much less reliable than the previous two as UDP connections are stateless by nature. Infact, when run with sudo privileges, nmap defaults to SYN Scans, otherwise it defaults to TCP scan. It is also to be noted that SYN scans also require sudo privileges because it needs to craft raw packets. However, it is not advisable to run SYN Scans on production environments as it might break certain unstable applications. Often, SYN Scans are not logged by applications running on the ports as most applications start logging a connection only after it has been fully established which is not the case with SYN Scans.They might be able to bypass some primitive firewalls.This method is an improvement on the previous ones because: This prevents the server from repeatedly trying to make the requests and massively reduces scan times. In the previous method where we were sending back a TCP packet with the ACK flag set after receiving an SYN/ACK packet, now we would be sending an RST packet. SYN scans, also known as “Half-Open” or “Stealth Scan” are an improvement over the previous method. Also this method is extremely slow as it waits for the entire TCP 3 way handshake. This is not a very reliable scan technique as it is easy to configure a firewall rule to respond back with RST packets or drop all incoming packets.

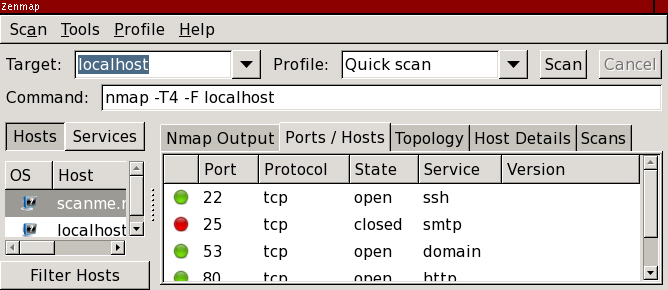
The target responds back with a TCP packet with the SYN/ACK flags set which would signify that the port is open and then Nmap would respond with a TCP packet with the ACK flag set and hence would complete the TCP 3-way handshake.Target doesn’t respond at all, probably due to a firewall dropping all incoming packets in which case the port will be considered filtered.The target responds with an RST packet that signifies that the port is closed.In this type of scan, Nmap sends a TCP packet to a port with the SYN flag set. Nmap supports a lot of different scan types. nmap -p- 127.0.0.1: This scans all the ports on the localhost.nmap -p 1-100 127.0.0.1: This scans ports from 1 to 100 on localhost.nmap -p 80 127.0.0.0.1: This scans port 80 on localhost.It can be a single port as well as a range of ports. Presently this enables OS detection (-O), version scanning (-sV), script scanning (-sC) and traceroute (–traceroute)
Deprecated format as users are now moving towards XML outputs.
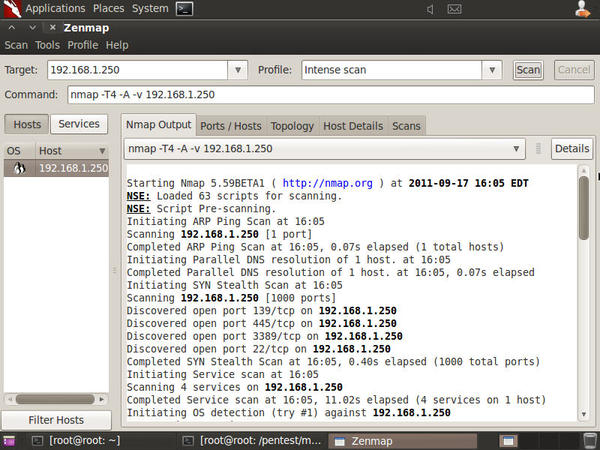
The minimum level of verbosity advised for use. You can even set the verbosity level as such :
#Zenmap commands mac#
It is essentially a port scanner that helps you scan networks and identify various ports and services available in the network, besides also providing further information on targets, including reverse DNS names, operating system guesses, device types, and MAC addresses. Nmap is probably the most famous reconnaissance tool among Pentesters and Hacker.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
